Why Dokdo is Korean Territory

Subjugation of Usan-guk
Usan-guk (Ulleungdo and Dokdo) was conquered by Ichan Isabu, and subjugated to Silla.
This is how Ulleungdo and Dokdo first became Korean territory.
It is recorded in the Reference Compilation of Documents of Korea (1770), that “Ulleung [Ulleungdo] and Usan [Dokdo] are both territories of Usan-guk.

Geography Section of the Annals of King Sejong’s Reign
It is recorded in the Geography Section of the Annals of King Sejong’s Reign, one of Joseon’s early government compilations, that both Ulleungdo and Dokdo belong to the Uljin county of Gangwon Province.
It specifically notes that “The two islands of Usan [Dokdo] and Mureung [Ulleungdo] are not located far apart from each other so Dokdo is visible from Ulleungdo on a clear day.” Dokdo is the only island that is visible from Ulleungdo without visual aid.

Abduction of An Yong-bok by Japanese Fishermen
An incident where the Korean fishermen An Yong-bok and Park Eodun were abducted by Japanese fishermen working for the Oya and Murakawa families while fishing in waters surrounding Ulleungdo, and taken to Japan.
A dispute over the ownership of Ulleungdo(the Ulleungdo Dispute) broke out between Joseon and Japan as a result of this incident.

Instruction to Inspect Ulleungdo
A diplomatic row broke out between Korea and Japan on the issue of sovereignty over Ulleungdo(the Ulleungdo Dispute) following the incident of An Yong-bok’s abduction. Subsequently, the Joseon government dispatched Jang Hansang, a regional official, to inspect the island of Ulleungdo.
Afterwards, the government of Joseon decided to dispatch officials to Ulleungdo to conduct inspections every two years, as proposed by Prime Minister Nam Guman.
<* This process of inspection was called “Suto”.>

The Tottori-han’s Submission
On December 24, 1695 the Edo Shogunate sent an inquiry to the Tottori-han to determine whether Ulleungdo was part of the Tottori-han.
The Tottori-han responded to this inquiry by informing the Shogunate that Takeshima (Ulleungdo) and Matsushima (Dokdo) did not belong to the Tottori-han, and thereby officially confirmed that Ulleungdo and Dokdo were not Japanese territory.

Order Banning Passage to Takeshima (Ulleungdo)
Having received confirmation that Ulleungdo and Dokdo were not Japanese territory, the Edo Shogunate ordered a ban on passage to Takeshima (Ulleungdo) on January 28, 1696.
Later, in a diplomatic correspondence with Joseon, the Shogunate officially acknowledged that Ulleungdo was territory of Joseon.

May, An Yong-bok’s Voyage to Japan
This was an incident where An Yong-bok sailed to Japan, chasing out Japanese fishing vessels which were fishing around Ulleungdo.
A historical document entitled, “Memorandum on the Arrival of a Boat from Joseon in 1696” records that An Yong-bok informed officials on Oki Island that Ulleungdo and Dokdo belonged to Gangwon-do.

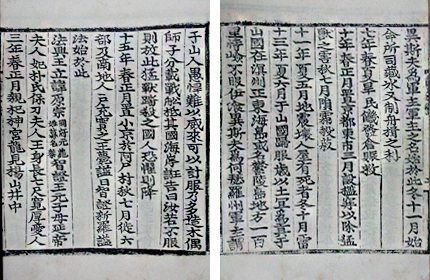
Dong'guk Munheon Bigo (Reference Compilation of Documents on Korea)
This is a government compilation which records Joseon’s civilization and institutions.
It is written that “Usando[Dokdo] and Ulleungdo… one of these two islands is Usan… According to <The Geography of Korea>, it is said that Ulleung and Usan are both territories of Usan-guk and that Usan is what the Japanese refer to as Matsushima [old Japanese name for Dokdo].”


Chōsenkoku Kōsai Simatsu Naitansho
(Confidential Inquiry into the Particulars of Relations with Joseon) <Replica>
Original Source : Dokdo Museum
Chōsenkoku Kōsai Simatsu Naitansho (Confidential Inquiry into the Particulars of Relations with Joseon)
This is a report submitted to the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs by an inspection team including Hakubo Sada.
This report, entitled “A Confidential Inquiry into the Particulars of Korea’s Foreign Relations” records of “How Takeshima [Ulleungdo] and Matsushima [Dokdo] came to belong to Joseon [Korea]” which reveals that the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs clearly recognized Dokdo as Korean territory.

The Dajōkan Order
This is an order given by the Dajōkan, the highest administrative body of Japan at the time, to the Japanese Ministry of Home Affairs, confirming that Ulleungdo and Dokdo were islands outside of Japan’s territory.
As a result of consultations with the government of Joseon (regarding the Ulleungdo Dispute), the Dajōkan concluded that Ulleungdo and Dokdo did not belong to Japan, and ordered the Japanese Ministry of Home Affairs as follows: “Regarding Takeshima [Ulleungdo] and one other island [Dokdo] about which an inquiry was submitted, bear in mind that our country [Japan] has nothing to do with them.”

Imperial Decree No. 41
This is a decree proclaimed by Emperor Gojong which stipulated that “Ulleungdo shall be named Uldo” and that “the post of inspector [dogam] shall be promoted to county magistrate [gunsu].”
Article 2 of this decree clearly stipulated that all of Ulleungdo, Jukdo and Seokdo (Dokdo) were to be placed under the jurisdiction of Uldo county (Uldo-gun).

The Shimane Prefecture Public Notice No. 40
This is a regional notice announcing the incorporation of Dokdo into Japanese territory.
Japan had been at war with Russia over its interests in Manchuria and the Korean peninsula since 1904, and needed the island to meet its military needs in the face of possible maritime clashes with Russia in the East Sea. Japan thus attempted to incorporate Dokdo in 1905 through this notice, claiming that the island was terra nullius.
However, Shimane Prefecture Public Notice No. 40 was issued as part of Japan’s gradual aggression against Korea’s sovereign rights. Because the issuance of the regional notice was an illegal act that infringed on Korea’s territorial sovereignty over Dokdo, which Korea had firmly established historically, the notice had no legal force under international law.

March, County Magistrate Sim Heung-taek’s Report
This is a report delivered to the acting governor of Gangwon Province and the Korean Ministry of Home Affairs (the equivalent of today’s Ministry of Security and Public Administration) by Sim Heung-taek, the then county magistrate of Uldo.
This report states “Dokdo, which is under the jurisdiction of this county…” which thus proves that Dokdo lay within the jurisdiction of Uldo county (Uldo-gun).
Directive No. 3
This is a directive issued by the Uijeongbu, the highest decision-making body of the Korean Empire, repudiating the incorporation of Dokdo into the territory of Japan.
The Uijeongbu received news from the acting governor of Gangwon province regarding Japan’s incorporation of Dokdo, and subsequently the Deputy Prime Minister of the Uijeongbu issued this directive repudiating the incorporation.

January 29, Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers Index Number (SCAPIN) 677
This is a memorandum which mandated the governmental and administrative separation of Dokdo from Japan after the end of World War II.
The Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers mandated that “…Japan is defined to include … excluding (a) Utsuryo (Ullung) Island, Liancourt Rocks (Take Island) [Dokdo] and Quelpart (Saishu or Cheju) Island …”
June 22, Supreme Commander for the Allied Powers Index Number (SCAPIN) 1033
This is a memorandum following SCAPIN 677, mandating the prohibition of Japanese vessels or personnel from coming within 12 nautical miles from Dokdo.


Conclusion of the Treaty of Peace with Japan
Original Source : US National Archives and Records Administration (NARA)
Conclusion of the Treaty of Peace with Japan
The Treaty of Peace with Japan is a treaty which the Allied Powers concluded with Japan at the close of World War II.
Article 2(a) provides that “Japan recognizing the independence of Korea, renounces all right title and claim to Korea, including the islands of Quelpart, Port Hamilton and Dagelet.”
Among Korea’s approximately 3,000 islands, these three islands have been referred to as examples, and therefore, the mere fact that Dokdo is not named explicitly in the said article, does not suggest that Dokdo is not included among those territories of Korea that have been separated from Japan.


 Subjugation of Usan-guk
Subjugation of Usan-guk